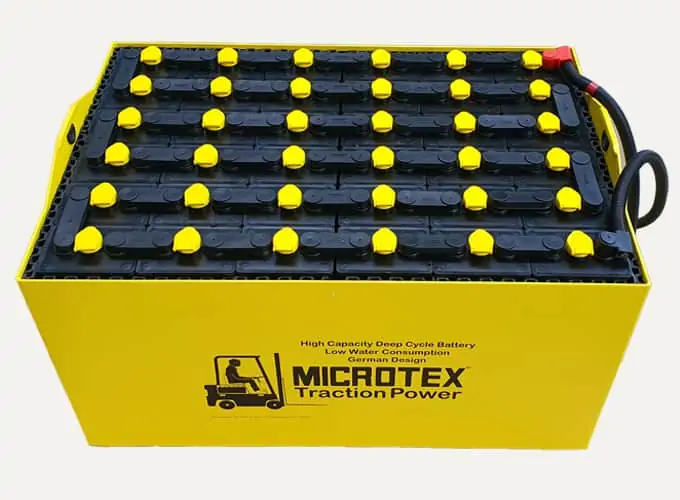
Bolt on Connectors vs Weld on Connectors
Technical Note: Superiority of Welded Lead Intercell Connectors in Traction Batteries
In the demanding environment of electric forklifts and material handling equipment (MHE), traction batteries are subjected to continuous shocks, vibrations, and mechanical stress.
A critical factor in ensuring the long-term reliability of these batteries lies in the robustness of the intercell connections.
Welded lead intercell connectors provide a permanent, high-strength joint that is inherently more secure than bolt on connectors. By eliminating the reliance on mechanical fasteners, welded joints remain unaffected by vibration or thermal cycling, which are common causes of bolt loosening.
When bolts loosen, they introduce electrical resistance at the connection point, often leading to overheating and, in severe cases, terminal melting.
From an electrical efficiency standpoint, welded lead connectors offer significantly lower contact resistance.
Bolt on connectors made from copper creates multiple interfaces—between the copper lug, bolt, and terminal—which are prone to micro-oxidation, torque relaxation, and eventual resistance buildup.
Welded connectors, in contrast, form a homogenous, continuous electrical path that ensures stable current delivery with minimal energy loss. This makes them ideal for high-current applications where electrical integrity is critical.
Over the operational life of a battery, even small resistive losses can accumulate into significant inefficiencies and heat-related degradation.
Corrosion resistance is another area where welded connectors have a clear advantage. Copper bolt-on connectors, especially when used in environments with poor watering discipline, are vulnerable to acid ingress.
Sulfuric acid splashes can enter the cable lug area, and through capillary action, the acid may travel along the copper strands, leading to internal corrosion. This not only weakens the conductor but also increases the risk of hidden failures.
Welded lead intercell connections, being lead and monolithic, are immune to this type of degradation and require minimal preventive maintenance. This enhances both safety and long-term performance, reducing unplanned downtime and associated costs.
Finally, the overall system design benefits significantly from welded intercell connectors.
While bolt-on systems are sometimes marketed as more “modular” or “modern,” they are better suited to temporary setups or applications needing frequent service interventions.
In contrast, welded lead intercell connectors are engineered for rugged, long-duration industrial use where traction battery packs are expected to run reliably with minimal human interference.
They offer a more compact and integrated design, improve vibration tolerance, reduce maintenance overhead, and ensure a secure electrical path throughout the battery’s life.
Welded lead intercell connectors are purpose-built for permanent, rugged industrial use where reliability, safety, and efficiency are non-negotiable.